Automatic logistics
Automatic logistics system refers to the automation and intelligence of equipment and facilities in the logistics operation process, including the overall design and implementation of three-dimensional warehouses, AGV automatic transportation systems, RGV automatic transportation systems, automatic picking systems, automatic identification systems, etc. The high degree of integration of modules realizes the comprehensive management and control of transportation, loading and unloading, packaging, sorting, identification and other operations, greatly improving the overall overall efficiency of enterprise logistics.
Related Products
Automatic logistics system refers to the automation and intelligence of equipment and facilities in the logistics operation process, including the overall design and implementation of three-dimensional warehouses, AGV automatic transportation systems, RGV automatic transportation systems, automatic picking systems, automatic identification systems, etc. The high degree of integration of modules realizes the comprehensive management and control of transportation, loading and unloading, packaging, sorting, identification and other operations, greatly improving the overall overall efficiency of enterprise logistics.
Three-dimensional warehouse
Also known as high-rise warehouse, automatic storage and retrieval system AS/RS (Automatic Storage & Retrieval System). It is a warehousing system based on high-level shelves, using computers for control and management, and automated storage and storage of conveying equipment. Automated warehouse is a key system to realize high-efficiency logistics and large-capacity storage, and plays a pivotal role in modern production and commodity circulation. Automated three-dimensional warehouse is the highest stage of the development of contemporary shelf storage systems. Together with automated sorting systems and automated guided vehicles, it is known as the three major signs of logistics technology modernization.
Basic advantages:
(1) Scientific storage and improve the level of material adjustment. As a warehouse, the three-dimensional warehouse first has the storage function, the system can carry out scientific management of the materials, make the materials reasonably stored, improve the processing efficiency, and adapt to the technological requirements of storage and production.
(2) Link production, speed up material turnover, and reduce costs. As an intermediate link in the production process, the three-dimensional warehouse should have the buffer storage function of raw materials, work-in-process and finished products. Under the conditions of automation and mechanized equipment processing, the degree of automation is improved, and the inventory cycle of various materials is shortened, thereby reducing the total cost.
(3) Provide an effective basis for the production command and decision-making of the enterprise. Automated warehouse is an important part of enterprise information system, especially in the integrated environment, logistics information system and enterprise information system become an organic whole. The leader of the enterprise formulates corresponding strategies and plans based on inventory information, directs, monitors and adjusts the production activities of the enterprise.
Yawei shares intelligent warehouse:
background:

Implementation scope:
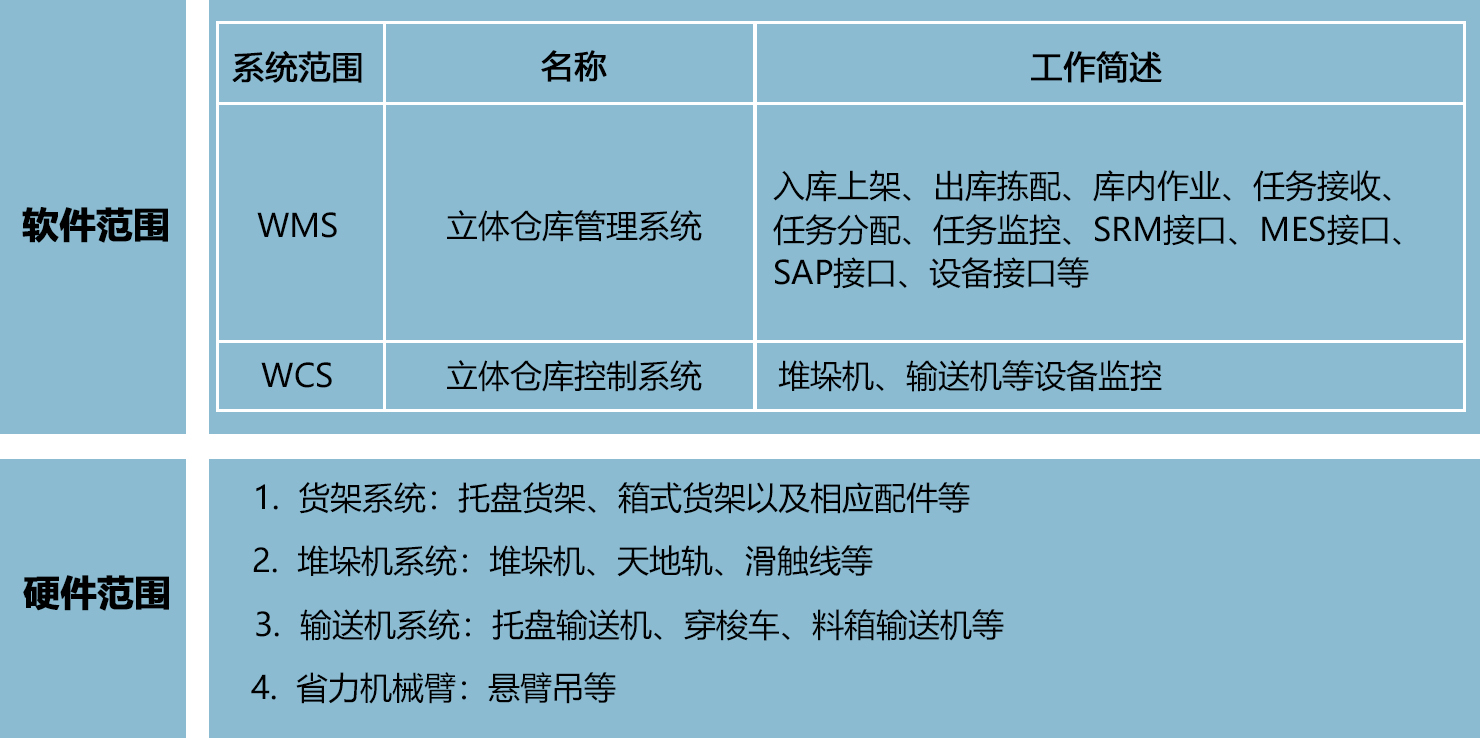
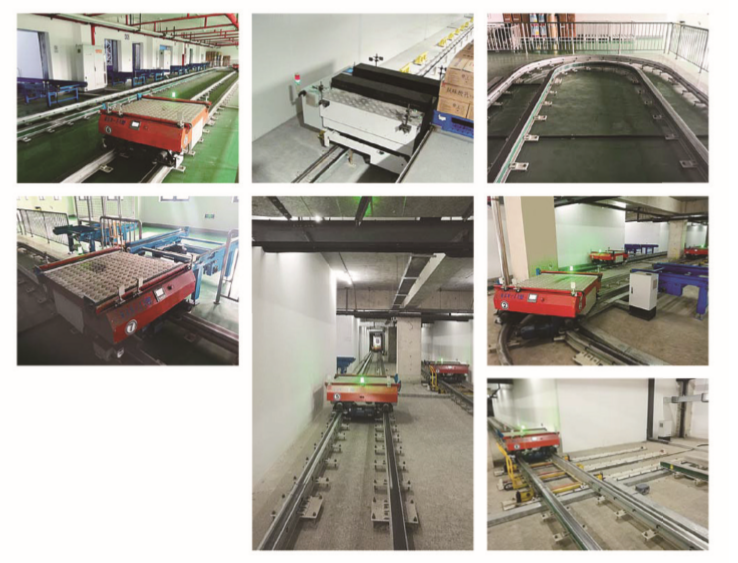
Implementation site map:
AGV(Automated Guided Vehicle)Automatic guided transport vehicle
AGV application scenarios:
With a variety of vehicles to adapt to different application scenarios. Including cage traction, roller docking, production material connection, production line docking; jacking function
It is suitable for the transportation of fixed shelves. By carrying racks (or pallets) to realize “goods to people” picking, effectively improving work efficiency,Reduce labor costs.

AGV dispatch system:
The AGV dispatching system interacts with the detection sensors, charging stations, pagers, AGVs, etc. of each station in a wireless or wired manner.
The system architecture is shown in the figure below:
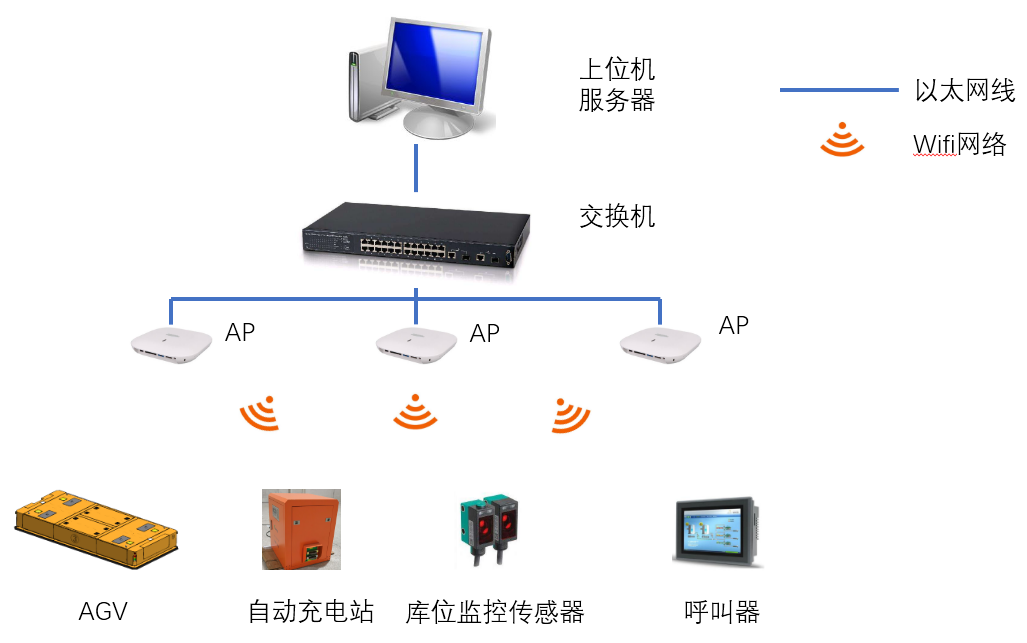
Dispatching system function:
Vehicle management: AGV registration management, no additional software development and modification are needed to add AGV later.
Map drawing: Draw the map path online according to the actual running path of the AGV.
Path planning: Before each task is executed, the optimal path is automatically calculated according to the algorithm to improve the operation rate of the AGV.
Task scheduling: Multiple tasks are executed in combination on the AGV allocation, and the AGV can also receive new tasks when the task is completed.
Vehicle scheduling: scheduling strategies such as the nearest selection, the longest idle time, the most sufficient power selection, the lowest utilization selection, and the first-in-first-out strategy for vehicle scheduling.
Traffic control: Avoid collisions and traffic deadlocks that may occur when multiple AGVs are in parallel.
Charging management: real-time monitoring of AGV power, when AGV power is lower than the set value, schedule it to recharge after completing the task.
Real-time monitoring: Real-time monitoring of the running status and position of the AGV.
Data report: The report includes AGV's historical tasks, performance, transportation volume, AGV status and predictive analysis reports, etc.
AGV system workflow:

RGV(Rail Guided Vehicle)Mechanism-guided vehicles: RGV can be divided into circular orbit type and linear reciprocating type. The circular orbit type RGV system has high efficiency and can work with multiple vehicles at the same time. Generally, aluminum alloy track is used; linear reciprocating type generally uses one RGV for reciprocating motion, and generally uses steel rail as the track. . Compared with the circular RGV system, the efficiency is relatively low. The RGV system can be used as the peripheral equipment of the three-dimensional warehouse, or it can be an independent system by itself.